Drinking (wine, ethyl) alcohol is widely used in the household: enters the composition of strong drinks and wines, it is used as a preserving agent in home billets of fruits, berries and juices. Especially it should be noted the healing properties of drinking alcohol, the main component of medicinal and healing tinctures that stimulate blood circulation, due to which it is used for compresses and rubbing (as an efficient external means).
Drinking alcohol is a colorless transparent liquid having a characteristic smell and taste, easily soluble in water in any quantities. Alcohol is lighter than water and therefore unevenly distributed in the volume of the aqueous mixture, concentrates more in the upper layers of the aqueous solution and in the brand. Specific alcohol density 0.791 g / cm3, boiling point - 78.3 ° C. Alcohol is hygroscopic and at high concentrations - 96-98 ° - actively absorbs water from the air, so it should be stored in tightly closed dishes.
Alcohol solutions with a high concentration of alcohol flammable, require cautious circulation and compliance with fire safety rules.
An open flame should be avoided to heat alcohol, preferably the heat of steam.
For food purposes, only rectified alcohol obtained from sugar and starch-containing raw materials is used. It is drinking alcohol, which is used for the preparation of strong and healing drinks. The state standard is limited to the content of alcohol impurities: aldehydes, esters, sevoyous oils and free acids. With homemade, these rules must be observed.
The preparation of alcohol is a complex technological process of interaction between many components, which requires compliance with the temperature regime at individual stages. The following main stages of this process can be distinguished:
1) the choice and preparation of the feedstock,
2) fermentation
3) distillation,
4) Cleaning alcohol,
5) aromatization, i.e. giving alcohol of certain flavoring, aromatic and color qualities.
Choosing and preparation of baseline raw materials
Life experience has shown that its accessibility is the main criterion for choosing raw materials, i.e. minimization of costs for its acquisition. Most often, sugar are used as raw materials, but it should be remembered that sugar is not only valuable, and often a scarce nutritious product, while, depending on the geographical location of the region, other types of raw materials can be more affordable: starch, various grains, Sugar beets, potatoes, etc. For comparison, when choosing the source raw material, a table of output of alcohol and vodka from various types of raw materials is given.The choice of the type of source raw material determines the quality of the finished product in many ways. So, for example, alcohol from sugar beets and refuses is not suitable for the preparation of thin you
The socket varieties of alcohol, but it is better than many others suitable for simple, sharp and sharp drinks, which are relatively low cost. Alcohol from potatoes is a little better quality, but requires refinement (double distillation, additional cleaning). With appropriate processing, alcohol from fruits and berries is approaching high-quality category and applied to high-quality drinks. For the preparation of high quality drinks, we recommend using alcohol obtained from starch raw materials (wheat or other grain).
In addition to the starch and sugar-containing products for the preparation of drinking alcohol, yeast, water, mineral and aromatic substances are necessary.
* Under vodka is a 40% alcohol solution. The basic value of this type of raw material is high in it starch (15-70% and even more), as well as sugars (2-6%). The starch content in farm crops is shown in the table below.

Flour and grain include the same chemicals, but the content of starch and sugars in flour is larger, which determines its greater value as raw materials for the preparation of alcohol.
Starch is the main carbohydrate potatoes and the flour of cereals, has the ability to swell, it is braided and converted by enzymes into simple sugars, which in fermentation go into wine alcohol. For transformation into sugar starch is subjected to precipitate. This operation is carried out in a liquid medium at elevated temperature and in the presence of a special substance (enzyme) - diastasis, which is contained in the malt.
Starch can be stored for a long time, easily precipitated, has a high alcohol production value and occupies the smallest volume when stored, which makes it the most profitable raw material for obtaining alcohol.
Theoretically, 716.8 ml of anhydrous alcohol can be obtained from 1 kg of starch. In practice, this figure is lower and largely depends on the quality of raw materials and strict compliance with the conditions of all the operations of the process of cooking alcohol.
Potatoes ranks first in the ease of extracting starch and transform it into sugar. Clasting temperature of potato starch, i.e. transition to soluble condition, - 55 ° C. To increase the release of alcohol, it is better to use potato varieties with a high starch content (20-25%). Determine the content of starch in potatoes is easy. First we need to weigh, for example, 5 kg of potatoes in air in a light bag or grid, and then re-weighed this potato, dropping it into the water and without removing it. The weight of potatoes will be much smaller. Depending on the weight of potatoes placed in water, according to the table below, the starch content is determined and the alcohol output from the amount of raw material is calculated.

Rye contains starch, which is braided at a relatively low temperature and is easily precipitated. Rye flour contains soluble proteins - organic nitrogenous substances, but does not contain gluten, which makes the stroke more liquid, and therefore more suitable for fering.
Soluble oils of rye flour make up the main type of yawning nutrition of yeast when fermented, which allows not to use additional mineral nutrition.
Wheat contains starch, which is harder to be removed braiding at a higher temperature of 65 ° C. In addition, wheat flour contains insoluble proteins, which, when swelling, form gluten, which attaches the drain of excessive luxury and drift.
Since a thick jam is less intensively fermented than liquid, gluten is desirable to separate from starch by washing the test.
To do this, first the flour is kneaded with water in a ratio of 1: 1 and withstand 20 minutes, then wash the dough with cold water, the volume of which is 3 l per 1 kg of flour.
When laundering, the dough is placed in a sieve, immersed in pelvis with water and washed. The gluten remains on the sieve and is removed, and the starch is washed away with water in the pelvis and is used to prepare. Other agricultural crops, including wild, containing starch in sufficient quantities, as well as cereal and cuisine waste can also be used to obtain alcohol. This type of raw material includes different cultures containing various types of sugars. Such cultures include, for example, sugar beets are also used apples and other fruits and berries (see Table).

Most of these cultures contain sugars less than 10%, which does not allow to obtain alcohol solutions with a high content of alcohol (more than 12%).
It should be borne in mind that in the juice obtained from fruits and berries, contains many acids that depress the activity of yeast. Therefore, in order to increase the concentration of sugars and reduce the acidity of the congestion, the juices are subjected to special processing: neutralization and brewing.
Sugar beet contains complex sugar sugar, which is directly yeasting, but decomposes under the action of yeast enzymes on simple sugar, and these sugars are then ferments. Therefore, the period of fermentation of beet sugar is longer than starch or fruit.
Apples occupy second place in the production of alcohol and wines after starch raw materials. They contain simple sugar - levular, which is directly fering yeast.
Sugar grapes and fruit glucose, as well as sugar berries - fructose fermented fairly easy. In addition to cultural plants, sugar and starch are contained in wild plants. These plants can be found in the forest, in the meadow, in the outskirts of fields and swamps, on shallow bays of rivers and lakes (see table).
Acorns are of particular interest, because they are easy to find and collect. Contain about 57% starch and up to 10% sugars. Tubils give the acorns knubber, bitter taste and depress the development of yeast. If you remove these substances, then a good starch product is obtained, suitable for obtaining alcohol. Tubils are easily removed by soaking. For the preparation of alcohol from the acorns make mezg. For this, the acorns collected by mature at the end of September are purified from the peel, each is cut into several parts and poured with water for two days. Then the water is drained and again poured acory with clean water (in the ratio of 1: 2), heated to a boil, is cooled and drained, and acorns are passed through the meat grinder. The resulting mass is dried. The dried acorns are intense or grind into the flour, which is used for the preparation of alcohol just like the flour of rye, wheat or other cultures.
![]()
Kishtan Konsky contains a large amount of starch, so it can be used to obtain alcohol as well as acorns. The fruits of Konsky's chestnut contain tubyl substances that need to be removed by soaking. Processing chestnut fruits as well as acorns, getting flour.
Icelandic lichen contains up to 44% soluble starch (lichhenin) and up to 3% sugar. A lichen is growing in pine bodies on sandy soil in the form of curly bushes with brownish ribbon blades with a white lining. Icelandic lichen is harvested throughout the year. First of all, bitter substances are removed from the lichen, for which it is soaked in water with soda (5 g of soda per 1 liter of water), then washed with clean water, they are soaked in clean water, then dried and crushed into flour. For soaking 1 kg of lichen 16 liters of soda solution. Grinding lichen is used to prepare alcohol.
Rhoves Rhoze, cane and other plants growing on swamps, along the banks of rivers and lakes contain a significant amount of starch. From rhizomes prepare flour, which is used for the preparation of alcohol.
Rogoz - a plant with high stem, straight long leaves, having upstairs inflorescence in the form of a black card, is widespread and well known. Dry rhizome rhoze contains up to 46% starch and 11% sugars. Rhizer's rhizome is purified from small roots and dirt, wash and cut on slices with a thickness of 0.5-1 cm. Dried in the furnace until they are broken with dry crash. Then the rhizomes are crushed to the state of flour.
Cane ordinary (trust) is one of the most common marsh plants. Dry rhizer cane contains up to 50% starch and up to 5% cane sugar. The rhizomes of the cane in spring or late in the fall, when the largest quantity of starch and sugar accumulates. To obtain flour root, dried, crushed and grind.
An ordinary graonist is a water plant that can often be found in small water bodies. It has characteristic shooting leaves and during flowering throws a long floral arrow with white three-fledged colors. Solid starchy plant. In the underwater part of the plant at the ends of the rhizomes, small tubers are formed by weight until 14 g. From one plant, 12-15 tubers are collected. In the tubers of the grains, it contains a lot of starch: in dry - up to 55%, in raw - 35%; Sahars up to 7%. The tubers are boiled, cut into small circles and dried. Of the dry tubers get flour, which is used as starch.
Susak umbrella - high (up to 1.5 m) plant, which is found everywhere on shallow coastures of rivers and lakes, along the edges of the swamps. The plant has a straight stem with a beam of a reprehensive leaves, on top of the stem is inflorestection in the form of an umbrella with beautiful white and pink flowers. Kryvica root in dry condition contains up to 60% starch. The rhizomes are purified, wash, cut into parts and dried, after which they will crush and get flour.
Rocket reeds - a perennial plant with high cylindrical stems, almost devoid of leaves. The reed is widespread, grows in thickets of coastal strip of shallow water bodies. The roots of the root contains a significant amount of starch (up to 43%) and sugars. Of the dry rhizomes, the reasons make flour that is used to prepare alcohol.
Burning large is a widespread plant in many regions. The roots of the burdock contain up to 45% of special starch (inulin), which can be turned into sugar. For this, the roots are welded for 2 hours in a small amount of water with the addition of acetic acid (20-30 ml of acetic essence by 1 liter of water). After riving in an acidic environment, inulin turns into sugar. An excess of acid is removed by adding honey, scratched marble or drinking soda, and alcohol is prepared from the resulting sweet mass.
Juniper is a branchy coniferous shrub, growing in pine forests on the edges and for old defores. The fruits of juniper - hidden, contain up to 42% of sugars. Of them prepared wine and alcohol. To do this, first get a sweet syrup, which is then fermented and distilled: the fruits of juniper grind, poured with hot water and insist for half an hour. The fruits are then getting out of the water and press juice, which is boosted on a water bath to obtain the necessary concentration of sugar.
The process of fermentation of the main raw material can not do without yeast.
Yeast - single-cell organisms belonging to the simplest mushrooms, cultural races of yeast are used to prepare alcoholic beverages and alcohol. The role of yeast is determined mainly by their ability to ferment carbohydrates, i.e. split sugar on wine alcohol and carbon dioxide. For the preparation of alcohol (distillation), wine yeast is used, which are also used when baking bread.Yeast is distributed in a liquid medium in the form of a suspension, constantly rising up to current carbon dioxide, intensively interact with sugars of solution (wort) and capable of forming a large number of alcohol in a short time, and in addition, they are acid resistant, which is necessary, as fermentation always occurs in acidic Medium. The yeast is well multiplied under normal conditions in a liquid nutrient medium, which includes nitrogenous and phosphorus substances and acids.
For the preparation of alcohol at home, pressed yeast is used (10-15% of the mass of the feedstock) to immediately provide their dominant position in the wort of the congestion and neutralize the effect of "wild" yeast. Pressed yeast is sold in the form of bars weighing 100-1000 g, but it is possible to grow yeast in the desired quantity.
Ordinary yeast in the production of alcohol can be replaced by other products, such as tomato paste. Depending on the concentration, it takes 2-3 times more than yeast. Use for these purposes and decoction of hops. Before entering into the solder, yeast is grown in a separate vessel on a sterile nutrient medium for 15-19 hours. The most suitable material for nutrient media is: green barley malt, rye flour, sugar waste.
For the nutrition of yeast, it is usually not enough organic nitrogen that is part of the protein compounds of raw materials. The absence of nitrogenous and phosphorous compounds in the solder of nitrogenous and phosphorous compounds, as well as oxygen leads to a decrease in yeast activity, which delays the process of sagar fermentation, so mineral substances are additionally made in the form of ammonium salts and phosphorus-containing compounds: ammonium chloride, ammonium sulfate, superphosphate or phosphorous diamamonium. All these substances are well known to gardeners and farmers.
The alcohol is a product of yeast of yeast, but when the Fortress of Braga reaches 15 °, most of the types of yeast dies, regardless of the presence of a sugar in Zakvask.
One of the main components of the yeast and the main starter is water. Water also use for washing raw materials and equipment.
The water used for the preparation of alcohol should meet the hygienic requirements for drinking water. It should be transparent, colorless, not to have odor and extraneous lifting, and besides, soft, with a small content of magnesium and calcium salts.
Boiled water for cooking should not be applied, because it practically does not contain dissolved air necessary yeast.
Natural water does not always satisfy the listed requirements, so it is purified by settling and filtering through special coal filters.
Mineral substances in the form of small additives are used to maintain yeast activity when fermentation fermented. Azotist and phosphorus-containing compounds are used, as well as acids.
Charcoal, caustic (washing) soda, aromatic substances and traditional spices are used to eliminate unpleasant odors of alcohol and beverages.
After selecting raw materials, the next stage is its preparation.
The most simple, economical and technological way to prepare raw materials for the preparation of alcohol at home, especially in the city apartment, is the use of sugar, yeast and gusty peas as raw materials. They are taken in the ratio of 1.0: 0.1: 0.2 and 3.0 parts of the water. Peas are boiling in boiling water for 12-24 hours, fall asleep into the container, poured sugar and yeast divorced in warm water and closed with water shutter. After 7-10 days, Zakvaska is ready for distillation. If you add milk to this mixture in a proportion of 0.2, then this process is accelerated to 3-4 days.And although the starch containing raw materials can be cheaper than sugar, but in the urban apartment, the technology of training is very laborious and creates a lot of inconvenience, which makes it difficult to use it.
Another thing in the countryside and in the country. There there are more favorable conditions for the use of this raw material. Preparation of starch-containing raw materials is to prepare malt and malt milk, processing starch-containing products and preparation of yeast yeast.
For the preparation of malt and malt milk, it is necessary to germinate grain of cereals. Periods of germination of grain for different crops are as follows: 7-8 days for wheat, 5-6 days for rye, 9-10 days for barley, 8-9 days for oats and 4-5 days for millet. In the grain, active enzymes are formed in the grain, which significantly accelerate the precipitation of starch. If necessary, malt should be dried, but after drossing, the activity of enzymes falls by 20% and accordingly increase the periods of germination.
The preparation of malt consists of a number of mandatory operations that include grain sorting, soaking, germination, cleaning from sprouts and drying. We will analyze these operations on the example of barley.
The grain is sifted through a large and fine sieve, then it is washed 2-3 times in hot water at a temperature of 50-55 ° C. The grain is soaked in pure wooden or enameled dishes, filled with water half. The pop-up grains and garbage are removed. The grain is better to pour out to the water gradually - it is easier to remove the accumulated garbage. Water should be changed every 7-8 hours. When it is discovered that the husk is easily separated from the pulp, the skin of the grain is proper and the sprout is denoted, and the grain itself does not blame, soaking should be finished and moved to the malt germination.
To do this, in a dark room, the grain scatter with a layer to 3 cm and covers with a wet cloth. The room should maintain a temperature not higher than 17.5 ° C and humidity not lower than 40%. The first 5 days of grain every 6 hours are ventilated, turn over, and the fabric is moisturized. Then, to reduce the loss of starch, the inflow of air into the room is limited, and the increase in temperature in it to the days remaining until the end of the process is trying to prevent, stirring and cooling the grain.
The main signs of cessation of growth: the length of the sprouts reached 5-6 mm, and the roots are 12-14 mm, the grains lose the flour taste and crushed and smell like a pleasant cucumber smell, and the roots are connected with each other.
After that, the malt is scattered in a warm dry room and rolling. Then the malt is dried in the dryer until its humidity is 3-3.5%. The temperature during drying should not exceed 40 ° C. When malt is ready, it is dry to the touch, smaller than before drying, and the roots are easily separated by friction in their hands. The malt is shaved with their hands, separated the sprouts and sieved on the sieve. Store the malt in a closed container in a dry room.
The stage of preparing a solution of germinated raw materials is also called the preparation of malt milk. For this process, it is preferable to use a mixture of malt: barley, rye and seed in a 2: 1: 1 ratio. A mixture of malt was poured with water at a temperature of 60-65 ° C, withstand 10 minutes and water is drained. The mixture is then finely melted in a coffee grinder or in a mortar, and then poured with a new portion of water at a temperature of 50-55 ° C, mixed thoroughly (for this it is better to take a mixer to obtain a homogeneous white liquid. Water is first not all, and 1/3 or 1/2 volume.
Mixed malt flow rates for raw materials of various species can be seen from the following table.

The processing of starch-containing raw materials involves the liberation of starch from cells and translating it into a soluble state. This is achieved by the temperature processing of starch with water. The starch grains are absorbed by a large amount of water with increasing temperature, they are tested, increase in volume and passed into a soluble state. As a result, starch is easily subjected to precipitate (ferment hydrolysis). The processing of potatoes consists of washing, grinding tubers, ribbling and training.
Potatoes are smelled in warm water, while for better purification, potatoes are kept in warm water 1-1.5 hours. Mocked tubers, changing water several times, the last water should be transparent, without a mut. With a small amount of potatoes (up to 10 kg) for washing, you can use conventional washing devices (brushes, washcloths, etc.).
They crush potatoes using any grieving devices that are at hand. In Kashitz, after crushing there should be no particles of more than 3 mm. To facilitate this operation, potatoes can be booked first, and then smolden and, adding water, skip through the sieve (colander).
Rilable potato mass on a water or sandbreaker for 1.5-2 hours. Then the mass is cooled to 65 ° C and starch precipitation is carried out.
The processing of flour of grain crops includes mixing operations with water, braysterization and riving. The flour mass is welded in the same way as potato, with a slightly sulfuric acid (0.5-0.8%). For riving, you can use pressure cookers that reduce the process duration up to 70 minutes.
Getting starch. Upon receipt of starch from potatoes, it is thoroughly washed with a brush and, without cleaning from the peel, a clutch on a shallow grater to get potato mezdu. The mezdu is put in a canvas bag, tie it and placed in a pelvis with cold water. After that, the bag is crushed with hands or a wooden pattern until the milk-colored liquid flows out of it; Water in the pelvis is changed and, if the water remains transparent, the departure of the mezgi stop. The dairy fluid should be given to stand three hours. When white dense sediment is formed at the bottom of the pelvis, the water from above is carefully drained and poured clean in the pelvis. Starch is stirred again with water, allowed to stand and pour water again. The resulting washed precipitate is and potato starch. Of 1 kg of potatoes, 150-200 g of dry starch are obtained.
In the same way, you can get starch from wheat flour, prepared pre-steep dough, and then flushing it in a linen bag. However, the starch of grain crops is more convenient and cheaper to receive not from flour, but from the grain. Due to the presence in the grain of gluten, extract starch with simple washout fails, therefore, for the preliminary decomposition of gluten, the fermentation method is used. For this grain, first soaked in water until they become easily crushed with your fingers. Then they will be crushed into a stage or passed through the meat grinder, placed in a vane for fermentation and poured warm water. For acceleration, fermentation is added to Chan a little frkop, which remained from the previous shutter. Soon, natural fermentation begins and gas bubbles appear on the surface.
As a result of fermentation, organic acids are formed dissolving gluten, but not destroying starch. By the end of the fermentation (for the 6-7th day), the separation of gas bubbles decreases and the surface of the liquid is covered with a solid fleece of fungi. Successful water should be drained, and rinse a fragmented grain mass through a sieve or linen bag. Then water defend and get starch in the sediment. Of 1 kg of grain, 400-500 g of dry starch are obtained.
In the same ways you can get starch from immature apples, pears and other plants, including wild. Starch, obtained from various types of raw materials, is precipitated to obtain sweet wort.
Recycling of sugar-containing raw materials involves obtaining sweet beets from sugar beets, apples and other fruits and berries.
Sugar beet contains sugar, which is included in the cellular juice and can be extracted as a solution by washing the beetted chip in hot water. Preparation of this type of raw material includes: cleaning beets, grinding roots in a fine chips, chip treatment with hot water, extraction of juice, neutralization and boiling of juice to obtain the wort of the desired concentration (15-18%) sugar. For this, the beet chip must be kept in a water bath at a temperature of 60-70 ° C, since the juice is not extracted from the crude beet.
After thermal treatment, the beetral mass is pressed, getting juice containing up to 15% sugar. To increase the sugar concentration to 18-20%, the juice is welded, and water or chalk in the amount of 20-30 g / l of juice are added to it to neutralize acids. Juice is filtered and used to prepare the wort.
Fruit-berry raw materials contains sugar, which is directly fermented with yeast, and therefore the preparation of raw materials is less laborious. The raw materials of this species wash, crushed and press the juice from it, which is then boosted and neutralized. After cooling, the juice is filtered and fermented.
Issues of optimizing the use of various types of fruit-berry raw materials are reduced to the choice of one or another species in terms of the ratio of the indicators of sugar and acidity presented in the following table.
Getting a yeast break is to prepare a sweet wort and subsequent introduction of uterine yeast into it. Sweet wort can be prepared by precipitation of starch raw materials or using sugar raw materials. The wort is prepared two days before the preparation of the main congestion as follows. Take a barley malt in the required quantity, depending on the weight of the supplision and the volume of the future starter (on 2 kg of flour supplies of the main plot, take 7-8 liters of water and 1.5-1.6 liters of prepared yeast stroke).
In the yeast chhan (3-liter pan) poured 1.5 liters of water and heated to 35 ° C. Then the rye flour (120 g) is slowly nomed into the water and thoroughly stirred to obtain a homogeneous mass. This flour plum is slowly heated on the sandy bath, bring to a boil and boil over 1-1.5 hours. The plot is cooled to 60 ° C, the crushed malt crushed into it and stirred for 5 minutes, then the pitch is covered with a lid and leave a mass for precipitation, maintaining the temperature in the range of 50-55 ° C. At such a temperature, the plot is kept 2-2.5 hours

And check for taste: it becomes sweet, then the mass is heated to 60-63 ° C and withstand another 2 hours. After that, the wort is filtered through the sieve, separated thick, sterilized at 85 ° C for 20-30 minutes, cooled to 50 ° C and make mineral powered: ammonium chloride 0.3 g / l, superphosphate 0.5 g / l, pre- Dissolved in hot water. Then the wort is acidified with sulfuric acid to acidity of 1% (100 g of 10% acid per 1 liter of Sousse).
Sweet wedge based on sugar raw materials is prepared as follows. By 1.5-1.6 liters of water, 250 g of sugar are taken, dissolved and heated to a boil. Then cooled, mineral power is added, acidified the previously indicated method and are used to grow yeast.
Then they produce seeds of seed (uterine) yeast. Pressed or dry yeast in the amount of 60-80 g is dissolved in 200 ml of cooled wort, they are thoroughly stirred and poured into a yeast chan at 30 ° C. Then the wort is cooled to a temperature of 15-16 ° C, covered with a lid and leave for ripening yeast.
After making yeast, the fermentation of wort begins and its temperature rises to 27-29 ° C. With increasing temperature, more than 30 ° C is cooled forced. To ensure the breath of yeast, the wort is twice an hour beaten for 1-2 minutes. After 6 hours, the concentration of the wort (taste or sucrometer) is checked. The feeling of sweetness should decrease, and at a concentration of 6-7% (by sucrometer 1.020-1.025) the devil of yeast ends. Mature yeast is used to ferment the goat. Aging continues 18-20 hours.
In the absence of ready-made yeast, use self-made. At home, yeast to ferment the wort is easy.
The first way. 1/2 cup of wheat flour poured 3/4 cup of warm water. This mixture is daily poured on a tablespoon of warm water every day. On the fourth day, we fight, stirring, on a weak fire, after which it should be cooled and pouring a tablespoon of flour. This operation is repeated 2 times in the next two days. The prepared mass is kept in the dishes, covered with a towel, at room temperature (20- 22 ° C). By the end of the week, yeast will be ready. Store them in a tightly closed glass jar in the refrigerator, not freezing, 8-10 days and use the same as pressed yeast.
The second way. Two tablespoons of hops (dried female hodges) are poured with two glasses of boiling water and boiled 5-10 minutes. The decoction is filtering through the sieve and once again bring to a boil. Then a glass of wheat flour is poured into clean enamel dishes and gradually pour and thoroughly mix hot decoction. Clean the capacitance with a clean towel, kept in a warm place of 1.5-2 days, after which the yeast is ready. A glass of yeast is put on 5 glasses of the congestion. The remaining yeast persists in the refrigerator 2-3 days, if you pour a glass of flour into them and let stand in heat for 4 hours. With further use, yeast is first diluted in a glass with warm water and placed 1.5-2 hours in a warm place.
The process of preparing the raw materials by rubbing (preparation) of the swax, which is to mix the supplies, their precipitating and the increase in mature yeast.
A 0.5 l of malt milk and as much cold water is poured into a large 10-liter pan. The mixture is stirred by a wooden stirrer (paddle), slowly adding the strained starch mass, and the temperature does not exceed 58 ° C. At a higher temperature, the frkine mass is cooled, the washing surface of the CHAN with cold water or passing water through the serpent, placed inside the coating chamber. In this case, it continues to intensively mix the contents of the chane. At the end of the mixing of malt milk and the starch mass, the temperature should not exceed 62 ° C. After that, the rest of the malt milk (0.5 l) is added and stirred from the solder for 5 minutes.
The calorie and water flow rate per 1 kg of supplies are given in the following table.

A mixture of malt milk and starch mass is kept in a water bath for 2 hours at 65 ° C, stirred and withstand another 2 hours.
The process of precipitation of the starch frustration usually lasts 3-3.5 hours, but with an old malt or retreat from the requirements of the technological process, precipitation can be delayed to 12-18 hours. At the same time, the temperature is maintained 55-65 ° C. In the countryside, Zakvask can be placed in the evening in a cooled furnace (50-60 ° C) and leave until morning. After precipitation, the taste of wort should be sufficient enough.
Starch is diluted with water, stirred to obtain starch milk. The starch milk is poured into boiling water and stir, not allowing the formation of a coolness. Boil must be maintained all the time and add starch milk gradually. Then quickly cool the solution to a temperature of 60-65 ° C. To the starch solution is valued with malt milk and stirred. The hovering solution immediately begins to dilute and after 3 minutes it turns out almost transparent liquid. This solution is left at a temperature of 60-65 ° C for 3 hours, during which the starch precipitation ends. After precipitation, the wort is filtered through the sieve to separate the husks and malt crushing, cooled and test.
If sugar or sugar-containing raw materials are used, then a little sugar (not more than 160-180 g / l of water) take sugar (not more than 160-180 g / l of water), the sugar is pre-dissolved in a small amount of water and heated to boil, cool and drained into the fermentation Chan.
Sushlo Razvasi is cooled to 30 ° C, the mineral nutrition is added (ammonium chloride 0.3 g / l) and mature yeast (yeast starter) from yeast chamber, stirred and continue to cool down to a temperature of 15 ° C, then the wort is drained into the fermentation Chan (20 l) and leave for fermentation in a dark place.
The fermentation Chan (pan, flask) is left at a temperature of 15 ° C and are not sealed, but only covered with a dense cloth. When fermentation occasionally, every 6-8 hours, mix the contents of the ferrous chamber to provide air and breathing the yeast.
Frying can be of different types: wavy, overflow, mixed and coating. All these types of fermentation are normal. However, the cover is considered normal for barley, oat and wheat starters, but if the potato frustration has coating fermentation, it means that yeast weakened and need to add young strong yeast. Fencing fermentation is undesirable, as often leads to splashing the wort and loss of raw materials.
To eliminate this disadvantage, a thick yeast dough is prepared, which is greatly fermented; Use only pure malt; limit the nutrition or breathing of yeast in Zapvask; Apply oat or salt malt; Foaming agents are used: vegetable oil and grained fat.
Frying is the main stage of the process of cooking, alcohol. The output of the finished product and its quality depends on how breaking. Frying is a complex chemical reaction that requires a strict temperature regime and a certain concentration of components. Schematically, this reaction can be represented as follows:
sugar -\u003e Ethyl alcohol + water + carbon dioxide
C12H22O11-\u003e C2H5OH + H2O + CO2
One of the important factors of the efficiency of fermentation is to maintain the optimal temperature (at least 18 ° C and not exceeding 24 ° C). So, a sharp cooling in the initial fermentation period can completely stop it, despite the fact that not all the sugar has sejected. At low temperatures, yeast remain alive, but cannot work. In this case, it is necessary to increase the temperature; Yeast will be able to continue working and bring to the end to the end, but for this it is predetermined to "outrage" with mixing them. The high fermentation temperature is much more dangerous, as it may be so weakened by the vital activity of yeast, which will not be able to resume their work. In this case, we recommend removing the rubber tube wort with yeast, add fresh and put the container into the room with a temperature not higher than 20 ° C. The rate of fermentation reaction in normal conditions is proportional to the sugar concentration in Zakvask, but it should be borne in mind that the reaction of the fermentation is terminated when the concentrations of the alcohol formed above 10 surround interest is reached. It follows that with insufficient sugar sugar, fermentation will occur slowly, and the surplus of sugar will simply not participate in the reaction of the formation of alcohol, which will lead to additional losses.
Frozening has three stages: initial fermentation - daisy, main fermentation and rating. In the initial stage, frivors are saturated with carbon dioxide, the temperature rises by 2-3 ° C, the taste of the solder first sweet, then sweetness weakens and becomes invisible. The duration of the initial stage is 25-30 hours.
With the main fermentation, the entire surface of the roasted is covered with large and small bubbles that form foam. The temperature rises to 30 ° C, and with a larger increase, forced cooling is required. The concentration of alcohol is rapidly growing, and the taste of the solder becomes bitter-sour. At the end of the main fermentation, the concentration of sugars in Zakvask drops to 1.5-3%. The duration of this phase is from 15 to 24 hours.
When finishing, the level of the swarm decreases, the foam settles, the temperature decreases to 25-26 ° C. The taste becomes bitterly sour from the presence of alcohol. The concentration of sugars is reduced to 1%, the acidity of the solder increases. The purpose of the change is to ferment the residual starch conversion products - dextrins. To do this, it is necessary to maintain diastasses in its active state, which can be achieved by observing the temperature regime during the precipitation process.
The rating of the potato congestion lasts 15-25 hours, but when using beet sugar, the rating lasts 90-120 hours.
Finally, the start-up soldered acquires a specific, slightly bitter taste; The formation of foam and the release of gas in it practically stops, although when the capacity shakes the capacity, the gas bubbles from the bottom are still rising. The smell also changes significantly and becomes sour-sweet from the sharp.
The ability to properly determine the moment of ripening of the starter is very important for getting a good alcohol. With distillation, its qualitative parameters are reduced by distrust, and the use of non-fermented ferry significantly reduces the end of the final product. However, the real ability to catch the moment when Rodsaw is ripe, comes with experience, because for each type of raw materials there are special signs.
Getting drinking alcohol
The distillation of the released starter allows you to get an alcohol solution of increased concentration. It contains from 8.5 to 14.5% alcohol, which corresponds to the testimony of the range of 0.987-0.990. When boiling, the swarms are formed by pairs containing several times (3-8) more alcohol than in solution that can be traced according to the table.
For flimsy distillation, it is necessary to mount a distillation cube, connect cooling, check the tightness of the connection of tubes and seals. Distillation can be carried out using various heating devices, including gas burners with open fire, but it is preferable to use closed thermal heating devices (TEN). With distillation, the solder is poured into a distillation cube, filling no more than two thirds of the cube volume, are closed with a compacted lid and heated. First, the heating is carried out at high speed (up to 5 ° C / min), then when the temperature is reached 70 ° C, the heating rate is reduced to 1 ° C / min. The temperature is measured by a thermometer of 0- 100 ° C.
The boiling of swax starts at a temperature of 90-93 ° C, depending on the concentration of alcohol. When the first chip appears, it is necessary to reduce the speed of heating, set the expiration rate of the outlet of 120-150 drops per minute and measure its temperature. At the otgon temperature above 30 ° C, cooling and water circulation in the refrigerator should be increased. Then it is necessary to stabilize the sweep rate of the ease of the ease and bring it to the maximum possible, but not allowing the release of the sourdot into the instrument pipeline. When distilcated, its temperature in the device's steamer will be slowly increased, and when it reaches 98.7 ° C, the distillation should be completed, since the content of alcohol in Zapvask is less than 1%, and, in addition, at such a temperature there is an intensive accumulation in the alcohol of the fusion oils.
In order to overtake the entire alcohol contained in the initial volume of the goat, it is necessary to overtake not more than one third of its volume.
One-time distillation gives outflow 3 times more concentrated. To obtain raw, i.e. crude, alcohol with a concentration of 80 ° distillation is carried out several times, the amount of distillation depends on the device of the distillation instrument. Some designs of distillation cubes make it possible to obtain an alcohol concentration of 72-80 ° after the second distillation. In the process of distillation, the solution temperature is controlled using a thermometer, and if it rose to 98.7 ° C, the distillation should be stopped.
Alcohol distillation after the first distillation is neutralized by the addition of caustic soda or ash birch firewood (10 g of soda per 1 liter of chip). For repeated distillation, the alcohol distille is drained into a distillation cube, filling no more than 3/4 of its volume. First heated intensively, and when the temperature is reached, 70 ° C reduce the heating intensity. The boiling point of the chip is within 85-87 ° C, to this temperature, the heating lead slowly. When the secondary chip appears, the heating rate must be increased and stabilized the maximum outflow of the outflow.
In the process of the second distillation, the concentration of alcohol is controlled in the receiver by means of an alcoholometer (hydrometer). Upon reaching the concentration of secondary chip 55-60 °, the resulting alcohol should be drained into another container and continue distillation of the second fraction until the boiling point rises to 98.5 ° C.
The resulting alcohol distillation of the second fraction with a low alcohol concentration (30 °) must be overtaked again. To do this, measure the amount of chip, as well as the volume of the obtained alcohol. The total volume of alcohol of two fractions obtained as a result of the second distillation is no more than 1/2 of the original alcohol chip.
The concentration of alcohol is approximately determined by the combustion method. For this, a small sample (20 ml) of alcohol is placed in a tablespoon and brought a lit match; The concentration of alcohol is determined approximately as follows: the ignition does not occur - a concentration of less than 30 °; ignition intermittent, with a flashing flame - a concentration of 35-38 °; Smooth sustainable burning with a high flame, aqueous residue less than half of the initial volume - the alcohol concentration of more than 50 °.
The output of alcohol depends on the type of raw materials and the quality of the execution of all operations. This indicator characterizes the efficiency of the use of raw materials and the qualification of the manufacturer.
Cooking brandy alcohol
For the manufacture of brandy alcohol, the wine material is first obtained by faving the grape juice. Suslo is prepared from grape juice, which is fermented for 3-4 weeks in closed containers under water shutter. This wine material is a victorious wort, it is subjected to multiple distillation, as a result of which brandy alcohol is obtained.Distillation of wine material allows you to get an alcohol solution of increased concentration. The victorious wort contains from 8.5 to 12.5% \u200b\u200balcohol. The distillation is based on the properties of alcohol concentrate in pairs to a greater extent than in aqueous solutions. For distillation, the wine material is placed in a distillation cube and heated to a boiling point, which, depending on the alcohol content, can be 83-93 ° C. When boiling, the wort is formed by pairs, which contain several times more alcohol than a solution (3-8 times). The process of the first distillation of brandy wine materials is carried out similarly to the process of producing drinking alcohol.
One-time distillation gives outflow 3 times more concentrated. To obtain raw, i.e. crude, alcohol use different distillation devices. Some designs of distillation cubes make it possible to obtain an alcohol concentration of 72-80 ° after the second distillation.
As a result of the first distillation, it receives outgonal in volume by no more than half of the initial volume of wine materials used in distillation (3 liters of chip is obtained from 6 liters of wine material).
Grape alcohol raw is subjected to re-distillation with separation on fractions: head, medium (brandy first grade alcohol) and tail. In Cuba remains a waste liquid.
The second distillation of the raw alcohol with the separation of fractions is a very responsible process, since the quality of the desirable alcohol depends on the proper selection of fractions and compliance with the required fusion speed. The second distillation is carried out in water heating devices.
In the second distillation, the head fraction of 82-84% by the volume containing a significant number of aldehydes, esters and higher alcohols, having a sharp smell and unpleasant taste, is first distinguished. This fraction is selected for 20-40 minutes in the amount of 1-3% of the volume of raw alcohol.
When a fortress distillate is achieved, 74-77% of the volume weakens the sharp smell, and from that moment you begin to select the average fraction (brandy alcohol). The yield of this fraction is 30-35% of the initial volume of raw alcohol. During the selection, the distillate fortress gradually drops and on average is 60-70% of the volume.
When the distillate fortress decreases to 50-40%, the volume is moving to the selection of the tail fraction. The volume of the tail fraction is 17-23% of the volume of raw alcohol. The exhaust liquid remaining in Cuba is 37-52% of the volume of raw alcohol.
The selected average fraction is a brandy alcohol, which is immediately laid in oak barrels for long exposure.
Fresh brandy alcohol is Babelessly, has a burning taste and not enough aromate. With excerpt in oak barrels there are significant changes.
The barrel is filled with alcohol at a temperature of 18-20 ° C, leaving free space (1-2% of its volume) for possible expansion of alcohol when the temperature changes. Filled oak barrels are clogged with tongs and installed in the storage. Stored cognac alcohol at an air temperature of 18-20 ± 3 ° C and humidity 75-85%. It is important to maintain a constant temperature in the repository. Pluntes are paraffinated to prevent alcohol losses. During storage in the barrels, the alcohol is tasting annually, tasting is carried out: check the color, alcohol content and acidity. Also check the state of barrels that should not have even minor leaks and inclination.
The length of exposure is determined by the appointment of alcohol and the composition of future cognacs. The longer exposure, the better the quality of cognac alcohols.
To excerpt brandy use oak barrels made of oak at the age of 70-100 years. Plates for barrels knee from sawn bars. The bitches disrupt the properties of wood, so wood with bitch is not used to prepare barrels. The volume of barrels is usually 30-50 liters. Old cognac barrels are great value, they cannot be used to store other liquids and wines. Cognac alcohol can withstand in metal tanks loaded with oak plates with a length of 60 cm, 1.8 cm thick and 6 cm wide at the rate of 100 cm2 of the surface on 1 liter of brandy alcohol.
Before laying, oak plates are washed, treated with alkali eating solution (0.5%) at a temperature of 15 ° C for two days. Then washed and dried. The plates are loaded into the tank, fasten with oak wedges so as not to float, and poured with alcohol. During excerpt in alcohol 1-2 times a year, oxygen is administered, overflowing it from the tank. The plates are used 3-4 times, then removed the upper layer (2-3 mm) and are reused. Alcohols are withstanding 3-5 years. After exposure from brandy alcohol, cognacs are preparing.
The fractions obtained after re-distillation (head and tail) are mixed, processed by manganese and caustic soda, allowed to stand for two hours, and then conduct a fractional distillation. The average fraction is used to prepare alcoholic beverages.
Cleaning drinking alcohol and its aromatization
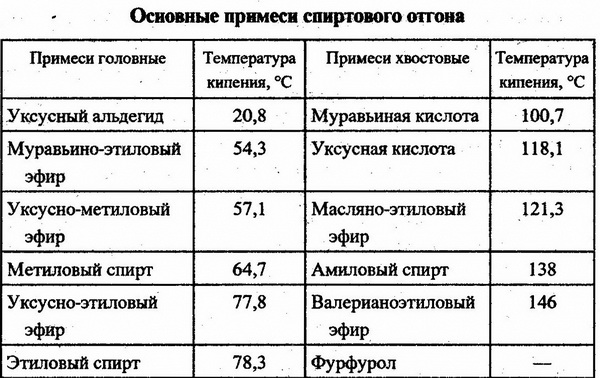
The obtained initial distillation of alcohol must be cleaned of harmful impurities and eliminate the characteristic unpleasant odor, the carrier of which is the fusion oils.The alcohol solution obtained from the starter, in addition to ethyl alcohol, contains a number of substances that need to be removed, as they are harmful and reduce the quality of the drinks. Purification methods include chemical purification using various substances neutralizing impurities, as well as separation of impurities by repeated evaporation and condensation of vapors, which allows to divide the composition into separate fractions and increase their concentration. The composition and temperature of boiling impurities are shown in the table below.
When cleaning, the acid is removed by neutralization by alkali or salts (soda), which are easily decomposed when heated or falls into the sediment. Syuvous Mas.
La is washed and translated into a non-volatile state also when processing alkali, the remaining impurities are oxidized by potassium permanganate.
Then these impurities are removed during distillation.
First, the alcohol distillation is subjected to chemical processing, and then fractional distillation is carried out, in which the sequential isolation of the components of the alcohol chip. Easy-boiling impurities - heads - stand out at the initial stage of distillation, then a rather clean alcohol is distilled off and, finally, head-air impurities - tail.To remove harmful impurities (head and tail products) during distillation, a number of varieties - fractions are selected.
This process can be represented as a simplified rectification at home, where high-boiling and low-boiling alcohols are removed.
The volume of the first fraction is 3-8% of the total alcohol in the solution. This alcohol for food is unsuitable, it can only be used for technical needs. The volume of the second fraction containing sufficiently pure alcohol is 75-85%. This alcohol is suitable for food purposes. The latter fraction (volume 2-6%) contains a significant amount of sigh oil. This part is collected and distilled by reacting all the necessary conditions.
Cleaning by distillation can be carried out using the same devices as with simple distillation. However, special devices are used to increase the concentration and degree of cleaning. Cleaning of raw alcohol includes: first chemical cleaning, second distillation and second chemical cleaning.
First check the content of alcohol and acidity of alcohol chip (raw alcohol). In the presence of an acidic reaction to alcohol add alkali or soda to neutralize acidity (1-2 g alkali con or 5-8 g of soda per 1 liter). The alcohol is then treated with a solution of manganese, which is bred in a small amount of distilled water. On 1 liter of cheese alcohol take 2 g of manganese, pre-dissolved in 50 ml of distilled water. The alcohol and the heatman's solution are thoroughly mixed and left for 15-20 minutes to complete the chemical reaction. After that, they add alkali or soda again in the same quantity, stirred and leave for clarification by 8-12 hours. Then the alcohol is filtered through the linen tissue and conduct the second operation of the rectification - fractional distillation.
There are specialists who believe that the mangartee gives alcohol an unpleasant taste. (But this, as a rule, occurs if there is no second distillation.) As an alternative to the use of marring, the following two options are offered.
Option number 1. In a three-liter bottle with the first distillation alcohol, a bunch of black currant twigs, cleaned from the bark, approximately 15-20 pieces, is placed, and remains in a bank for about two weeks until the contents are spoken.
Option # 2. A filter is collected in which the role of the filter element performs potatoes sliced \u200b\u200binto cubes of about 0.5-1 cm. They are filled with a plastic bank from under carbonated water by about 3/4, and the first distillation alcohol alcohol is driven through this filter.
According to these professionals, these techniques are completely replaced by the use of potassium mangartan (mangalls).
To clean the alcohol by the second distillation, it is necessary to assemble the second device, which can be used a distillation cube with a drip.
Raw alcohol for distillation is diluted with soft water to a concentration of 45-50 °. The required amount of water is poured into a container with raw alcohol and measured the concentration of the alcoholometer (hydrometer). The diluted alcohol is placed in the apparatus (cube) and quickly heated to 60 ° C, then the heating rate is reduced and slowly heated to the boiling point, which is in the range of 83.5-84.5 ° C.
The first fraction of the alcohol obtained in the initial stage of distillation is drained into a separate container and in the future use only for technical purposes. The volume of this fraction is 3-8% of the volume of alcohol in the solution of diluted raw alcohol (40 ml per 1 liter of alcohol).
The second stage of distillation is carried out at elevated heating rate. The distillation should be conducted to a temperature of 96-97 ° C, after which the second alcohol fraction is obtained, which can be used for nutritional in the future. The volume of alcohol of the second fraction is 80-84% of alcohol volume in the solution of diluted raw alcohol (420 ml per 1 liter of alcohol). The second fraction of alcohol is poured into a separate container and conduct the second chemical cleaning.
At the third stage of distillation, which flows at a temperature of 96-99 ° C, a low concentration alcohol is obtained with a high content of sigh oil. This alcohol is accumulated in a special container and repeated rectification. The volume of the third fraction of alcohol is 8-10% of the volume of the second fraction (60-80 ml per 1 liter of alcohol).
When cleaning through the second distillation, there are several additional techniques that help achieve the elimination of the unpleasant odor and taste, which has the first distillation alcohol.
Firstly, this is adding fresh milk into the distillation alcohol in a proportion of 1: 6. Very effective and efficient cleaning method.
Secondly, adding several spoons of the table salt into the distilled alcohol and 100-200 g of birch coal.
The effect is not so pronounced, moreover, the smallest coal particles clog the coil and pipelines, which can lead to a temporary failure of the device.
Thirdly, adding different spices to the distilled alcohol - 5-6 black pepper peas, 5-6 laurel sheets, etc. The effect is also not expressed quite clearly. Chemical cleaning of the second (food) alcohol fraction is carried out by treating charcoal. For this, the alcohol is placed in a bottle and add the integral charcoal (lime, birch) in the amount of 50 g per 1 liter of alcohol. Alcohol with coal periodically, 2 times a day, shackle and insist for 3 weeks. At the end of cleaning, the alcohol is filtered through the linen tissue and through the filter paper.
In order to get high concentration alcohol close to 100%, it is necessary to further process the alcohol obtained after distillation and carry out the operation of dehydration, for which special chemicals are used, which are capable of attaching water and do not interact with alcohol. Such substances include chloride of calcium and well known to all gardeners copper vigor. These salts have the ability to attach and hold water in quantity, several times greater than the weight of the dry matter. But since the copper vigoros in itself is not a harmless substance, it is recommended to use Calcium chloride. It should be poured in a metal or porcelain dishes at a temperature of 150 ° C for 20 minutes and cool to a temperature of 30-40 ° C. In the alcohol obtained after distillation with a concentration of 70-80 ° to float the calcined calcium chloride, mix and give to stand for an hour. Then merge the dehydrated alcohol into the distillation cube and overtake. After distillation, the concentration of alcohol is 96-97 °. Such alcohol is very hygroscopic and should be stored in tightly closed dishes. On 1 l of purified alcohol, the fortress of 70 ° it is necessary to take 80 g of dry calcium chloride.
To verify the quality of the obtained alcohol after cleaning, you can spend at home in the presence of the necessary equipment a number of analyzes.
First determine the color and transparency. For this, alcohol is poured into a glass transparent vessel and visually define its color, shade and presence of impurities. Muddy, whitish shade testifies to the presence of sigh oil.
The concentration of alcohol is determined using a simple device - a alcoholometer, which is easy to make at home. The overall comprehensive check - the sample for purity - it allows us to generally assess the quality of alcohol.
The second oxidation check is carried out using a 1% solution of potassium permanganate, which should not change its characteristic raspberry in the mixture with alcohol for 20 minutes.
The alcohol must withstand the cleanliness test and oxidation check.
The presence of individual impurities: aldehydes, acids, ethers are determined by smell and taste, but the quantitative content of these impurities can only be determined by conducting chemical analyzes using special chemicals. Pure alcohol should not contain impurities more than 0.02 g / l of free acids, 0.02% aldehydes, 50 mg / l ether, 0.003% of the fursive oils, the presence of the furfural is not allowed.
To determine the color and transparency in a clean dry cylinder, a capacity of 100-150 ml from colorless and transparent glass poured alcohol and in the scattered light passing through the cylinder, tint and presence of mechanical impurities are observed.
Definition of smell and taste. A small amount of alcohol is placed in a vessel with a well-closing plug, diluted with 2.5-3.0 volumes of cold drinking water and after pre-severe mixing immediately produce alcohol tests on the smell and taste.
The alcohol fortress is determined by a metal or glass alcohol, using the data of the table below.
To carry out a sample for purity, 10 ml of alcohol is poured into a narrow flask, a capacity of 70 ml and is rapidly added to 3-4 receptions with a constant stripping of 10 ml of sulfuric acid (Ud. 1,835).

The resulting mixture is immediately heated on the alcohol lamp, which gives the flame with a height of 4-5 cm and the width in the lower (wide) part of about 1 cm. During the heating of the flask, the fluid is well stirred and that the fire does not touch the flasks above the boundary of the heated fluid. . The heating of the mixture is stopped when bubbles come out onto its surface, forming foam; The heating process lasts 30-40 seconds, after which the mixture is allowed to cool. The cooled mixture in the flask should be completely colorless.
For accuracy of testing the contents (after cooling), the flasks are transferred to a special cylinder with a fit plug and, using a tripod, observe the color of the mixture, comparing with alcohol, as well as with acid, taken in equal volumes and poured into separate cylinders of the same diameter and quality glass.
The test result is recognized as positive if the mixture will be as colorless as alcohol and acid.
To carry out a sample to oxidizing a cylinder with a fitting plug and a 50 ml mark rinse with alcohol, filled with the same alcohol to the label and immersed for 10 minutes into water, having a temperature of 15 ° C, poured into a glass bath above the level of alcohol in the cylinder. After 10 minutes, 1 ml of a solution of potassium mangartage was added to the cylinder (0.2 g of potassium waters), close the cylinder with a plug and, mixing the liquid, plunge into the bath with water. When standing, the red-purple color of the mixture is changed presidentially and reaches the painting of a special type solution, the appearance of which is accepted for the end of the test.
To monitor the change in the color of the alcohol under the cylinder put a sheet of white paper. The time during which the oxidation reaction occurs, is expressed in minutes. The test result is recognized as positive if the color is saved for 20 minutes.
The determination of acids and furfurol is usually carried out in laboratory conditions.
To determine the content of acids, 100 ml of the test alcohol is diluted with 100 ml of water and, mixing, boil in a flask with a ball refrigerator for 30 minutes. After cooling to a temperature of 35-40 ° C (the bottom of the flasks can be kept hand), while the upper part of the refrigerator must be closed with a tube with sampling lime, the acidity is checked. Acids alcohol are neutralized with 0.1 N of the caustic soda with phenolphthalene before the appearance of pink dyeing not disappearing for 1-2 minutes.
The number of milligrams of acids (G) in terms of acetic acid in 1 l of anhydrous alcohol is calculated by the formula:

Where V is the amount of 0.1 H solution of the caustic soda, used on the neutralization of 100 ml of the test alcohol, ml; 6- Number of acetic acid, corresponding to 1 ml of 0.1 H solution of caustic soda, mg; 10 - the coefficient of recalculation of 1 liters of alcohol; K - the coefficient of recalculation of anhydrous alcohol K \u003d 100; C is the fortress of the test alcohol,% (by volume).
To determine the content of the furfurol into the cylinder with a trimming capacity of 10 ml poured with a dropper 10 drops of pure aniline, 3 drops of hydrochloric acid (UD. 1.885) and bring the volume to a tag with alcohol. If a solution remains colorless for 10 minutes, it is believed that the alcohol stood the test. The appearance of red color characterizes the presence of furfurol.
As a rule, the alcohol, purified at home according to the above technology, meets the necessary requirements for drinking alcohol.
An important technique to significantly improve the taste and smell of drinking alcohol prepared at home is its aromatization.
To obtain a fragrance and giving a special taste alcohol, almost all edible berries and fruits, spices and some herbs, flowers and roots can be used. Typically, plants, with the help of which flavor drinks, are harvested in advance, dried and stored in closed containers. It is more convenient to store not dry plants, but make an infusion or decoction from them that occupy less space and are better saved.
Flavoring agents are extracted from plant raw materials with solvents - alcohol or water. Before processing, raw materials must be crushed. The easiest way to extract is to insist on alcohol. In the process of insteading, the alcohol is saturated with aromatic substances, the beverage taste changes. Raw materials should be insisted until all flavoring substances are dissolved in alcohol.
When insistered, the solution is periodically constricted, and then again poured the raw materials and shackle. The most effective plants give aromatic substances at the solvent fortress 45-50 °. If the alcohol is stronger, which is determined by the hydrometer, then the solution is diluted. Periodically changing the freshest flavoring raw materials, poured it with the same alcohol, obtaining an infusion of higher concentration. The same effect is achieved by boiling raw materials in a closed dish with subsequent insistence or without it. Boil time is 10-15 minutes. With the help of concentrated info, it is sometimes improved by alcohol, which has not passed the insteading step.
The duration of preparation of tinctures depends on the type of raw material and the temperature regime and is usually 3-5 weeks. With increasing temperature to 50-60 ° C, the time of the insistence of certain types of raw materials is reduced to 5-8 days. Such a tincture is called rare. If the bottles with an insisted drink put on wooden bars placed in a saucepan with water, and boil, then it turns out a good tincture.
The distillation of the beads allows to obtain concentrated solutions with a high degree of saturation of aromatic substances, as well as essential oils. These substances almost do not change the taste of the beverage, but give it the desired fragrance.
Not only chasters are distilled to accumulate fragrances, but also infusions. To do this, it is necessary to take some spice, finely destroyed, pour boiling water (to take 3.5 liters of water at 400 g), tightly clog and insist the day. Then add 2.5 liters of water and distinguish until the smell of spice is stored. Then add fresh spices and overtakes again. You can make this operation and for the third time. Such water is called Trohen, and if 200 g of such water pour into 1.2 liters of alcohol, then the taste of the resulting drink will be similar to that it turns out when distillation with spices.
The most complex method of obtaining aromatic substances is based on their evaporation by treating raw materials with overheated steam. To do this, use a special distillation apparatus, in which the raw material is exposed to superheated steam conducting a deep thermal impact on raw materials, which contributes to the best removal of aromatic substances. In this way, concentrated solutions and essential oils are obtained.
To give drinks the desired aroma, the resulting solutions in a small amount are added to the drinks in the manufacture. The composition of the components and their dose are of particular interest and make up the secret of making a drink.
In addition, the simple methods of distillation of alcoholic beverages are used, pre-served on several aromatic components, which allows to obtain good flavored drinks at home, in particular vodka, aperitifs and balms.
If plants and spices are added to Zakvask, then during distillation, the fragrance turns out to be weak. To enhance it, it is necessary to prevail the water to be prepared on the selected spices. You can make a decoction from them and to dilute Zakvask.
It is more preferable to prepare a solder on flavored water, as well as placing the flavoring agent into the drill. Such alcohol will have a steady fragrance without the slightest spherical smell of Syvuhi. For this, it is desirable to do the tubes between the furnace and a container, a container and a dry car in the form of coils and additionally warm them. You can warm up the alley itself, if it is made of metal. The essence of the process is to process flavoring with superheated alcohol-containing steam.
Distillation of infusions allows to obtain flavored drinks with high alcohol content. To give alcohol the desired taste after distillation, it is mixed with the values \u200b\u200bof plants, while the alcohol itself insist. For example, the alcohol infused on a lemon crust, after distillation insist again in fresh lemon crust.
Its features is to use spices for cooking. Spices can be entered into drinks in natural form and insist for some time, after which they are removed. Often spices are introduced in the form of an exhaust, which is pre-injected by insisting in a water or low alcohol medium. In strong drinks, spices are intensely dissolved, as a result of which the taste of the beverage becomes bitter and sometimes burning, so for sweet wines, it is preferable to use water spices with aqueous solutions. The table below shows the approximate doses of spices used to aromatize alcoholic beverages during insistence.
A good aromatic tool is berry alcohol, which is obtained by insisting a slightly rolled berry with a strong natural aroma (black currant, raspberry, strawberry, strawberry). For this, the berries are rolling into the sun or in the drying cabinet to such a state when they become dense, but still soft enough. Berries will interfere in a glass bottle, filling the entire volume, and poured 80-90 ° with strong alcohol, then clog and put in a warm place. The contents of the bottle 2-3 times a day shake. Insist within

7-10 days until the alcohol takes the color and aroma of berries. After that, the alcohol is drained and used for alcoholing berry wines having a weak natural aroma.
Alcohol is also prepared by infusion vanilla, which is poorly soluble in water. Directly into the drink vanillin should not be put, as it gives bitterness and worsens the taste. For the preparation of vanilla alcohol, it takes 5-6 teaspoons of vanillin, poured with alcohol (200 ml, 70 °) and insist for several days, then filtered and used for cooking. On 1 l of fluid take 50-100 ml of vanilla alcohol.
Essential oils and essences are widely across the aromatization of alcoholic beverages. They are concentrated aromatic substances and are used in a very small amount for the aromatization of large volumes

Pitkov. In some cases there are enough two drops of essential oil (for example, pink) to aromatize several liters of drink.
Essential oils from vegetable raw materials and spices can be obtained using a special instrument by distillation with water vapor.
The device for obtaining oils (Fig. 1) includes flask 1 with a volume of 1 liter, reflux 2, oil receiver 4. For distillation to the flask 20-50 g of spices (vegetable raw materials) and 500-800 ml of water are poured, and for uniform boiling In the flask lay small pieces of porcelain or shards of burnt clay 5. Inside the flasks using a durable thread 3 suspend the oil receiver so that the lower end of the refrigerator is above the receiver's funnel at a distance of 1-2 mm.
The receiver must be freely placed in the flask, without touching its walls, and be above the water level at a distance of at least 50 mm. The flask is closed with a plug, into which the refrigerator is inserted, and heated on the sandy bath. The contents of the flask are adjusted to a boil and support it for several hours until the increase in the volume of essential oils in the receiver will stop. The rate of condensate expiration should not exceed 50-55 drops per minute. When the essential oils are distilled off, the density of which is less than 1 g / cm3, i.e. these oils are lighter than water and are on the surface of condensate, the receiver with a bent knee of the tanning tube is used. In this case, the oil is on the surface, and excess water flows through the bent the knee of the receiver back to the flask.
When excluding oils with a density of more than 1 g / cm3, a direct receiver with a hole in the upper part is used. Oils accumulate at the bottom, and excess water flows into the flask through the hole in the receiver. The density of essential oils, which are often used to aromatize drinks, is shown in the following table.

In addition to essential oils used essences. These are concentrated solutions of aromatic substances that are removed from raw materials with solvents. As solvents, alcohol or vodka are usually used. Most often, citrus, flower and roma essences are used to aromatize beverages.
For the preparation of essences, grass and roots should be well dried and crushed. Mix them according to special recipes selected or invented for each type of essences. The mixture of crushed herbs and roots are poured with alcoholic mortar with a strength of at least 40 ° and insist not less than 8 days; Then, from this infusion of distillation, essences are obtained for the preparation of beverages. The implaced solutions are distilled in a special distilted Cuba, which has in the middle of a cylindrical metal grid (metal glass with holes), in which the crushed roots and herbs are located.
[Email Protected]


